Table of Contents
Welcome to GuideFlare.com, your gateway to unraveling the essence of research from an evolutionary perspective. Research, a relentless pursuit of knowledge, lies at the heart of human progress and innovation. In this article, we delve into the meaning, nature, objectives, process, significance, and limitations of research, shedding light on its transformational role in shaping our world. With GuideFlare.com as your trusted companion, embark on a journey to explore the depths of human inquiry and discovery.
What Is Research?
Research comprises of two words, "Re'" and "search". While "Re" implies a repetitive or iterative procoss, "Search" denotes making a thorough examination of or leoking over carefully in order to find something. Different researchers have defined research in various ways due to its wide scope. But, in general, researeh car. be defined as a scientific process where new facts, ideas, and theories arc established and/or proved in different areas of knowledge. Research aims at adding to the existing stock of knowledge for the betterment of world.
According to John Best, "Research is a systematic activity directed towards discovery and the development of an orga ised body of knowledge".
According to Waltz and Bausell, "Research is a systematic, Tormal, rigorous and precise process employed to gain'solutions to problems or to discover and interpret new facts and relationships".
According to Clifford Woody, "Research comprises defining and redefining problems, formulating hypothesis or suggested soiutions, Collecting, Orgarising and Evaluating ata, Making deductions and reaching Conclusions to determine they fit the formulaing hypothesis".
Research involves scientife and systematic analysis of a research area and concluding the findings with appropriate reasoning. It is a systematic as well as an object-oriented process. The process of research begins with identitying the research problem; following data collection, data analysis, and ends with conclude the findings. It should be conducted in an unbiased manner, without nanipulating the findings.
Research plays a vital role in management decision-naking by analysing the situation systematically and finding new ways to support the operations. For example, a company may conduct research to know the consumer reviews about certain products.
Research can be carried-out using various methods and techniques which are collectively called as research methods'. Research methods are the tools and techniques for analysing and collecting data so that meaningful outcomes can be extracted from the problem being studied. 'Research methodology' can be defined as the scientific procedure to solve various problems related to research. It has a wider scope than research methods. as in addition to the methods and techniques, the researcher designs different methodologies for different research problems. Research methodology varies according to the research problem. Therefore, it is concerned with the application of research methods as per the requirement.
Nature of Research
Nature of research is as follows:
1) Systematic Activity: Research follows a systematic procedure to analyse a research problem in a better way. A research cannot be conducted in a haphazard manner. A researcher can come to a step only when the previous one is completed.
2) Logical Process: The basic tenet of research is "logic". All the assumptions and analyses undertaken are based on certain logic. Research is a scientific, systematic, and planned investigation to understand the underlying problem.
3) Iterative Process: Research is an iterative process. Sometimes it becomes necessary for the researcher to review the work of earlier stages, which makes it cyclic in nature. Often it becomes harder for the researcher to find out the starting and ending points.
4) Based on Empirical Evidences: Research studies are empirical in nature. Every step in research is carried- out using various scientific tools and techniques. Every step in research is checked for accuracy and is based on observable experiences or empirical evidences. Therefore, quantitative research is easier to validate than qualitative research, which is more conceptual in nature.
5) Controlled in Nature: The researchers often control the effect of variables by allowing only some variables to vary so that their effects can be tested. Due to this reason, controlling the variables in, a scientific research is much easier than controlling the factors in a social research. Hence in research, it is very essential to control the variables carefully.
Objectives of Research
Research strives to achieve foliowing five objectives:
1) To Explore about Unknown: One of the prime objectives of research is to explore the unknown object or phenomenon. While exploring, a researcher tries to understand the details of the situation or phenomenon for developing preliminary hypotheses and generalisations. Exploring allows the researchers to develop theories and explains the questions of how and why a phenomenon operates in a particular way.
2) To Describe the Features: Research seeks to describe the features of a phenomenon. It is one of the core activities of research where a researcher either observes the phenomenon and records its characteristic behaviour, or conducts standardised tests to measure the behaviour, or describes the change in attitude or opinion of the object. For example, a researcher can describe the behaviour of smokers by either observing it, or analysing their behaviour by undergoing some standard tests, such as measuring the level of resistance, per day consumption, etc.
3) To Explain a Phenomenon: Another objective of research is to provide explanation. Here, the researcher aims to explain how and why a phenomenon operates in a specific way. The researchers develop certain theories explaining the behaviour of a particular phenomenon by determining the factors that cause the change and identifying their effects on the phenomenon. Most of the scientific and educational researches have this objective for their studies. For example, if a researcher is trying to know, "Do weekend parties for employee families improve work life balance?", then in this case, the cause is 'weekend parties' and the effect is 'work life balance'.
4) To Predict Future Activities: Research is also conducted with the aim of predicting the future activities. Prediction can be done on the basis of explanations regarding a phenomenon. Hence, having adequate prior information is essential for making forecasts. Forecasting activity can also be performed on the research based on explanation. Here, predictions are made on the basis of cause and effect relationships in a phenomenon. A good example of this objective is the research that analysts conduct during elections to predict the winning political party based on the information that they are able to gather from the voting polls.
5) To Influence Activities: The last objective of a research study is known as controlling or influencing particular phenomenon. Here, the research emphasises on applying the existing theories and models instead of developing new theories, for influencing various facets of environment. Most of the research conducted Behaviour and educational research falls under the area of influence.
Research Process
Discovering and analysing a range of significant and reliable information about a particular issue or problem with systematic planning is known as research process. This process involves several steps for complete analysis of the research problem. These steps are required for identifying and analysing important information about a research topic.
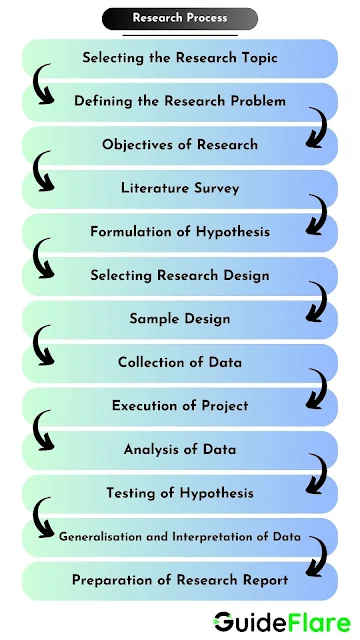
The steps of research process are described below.
1) Selecting the Research Topic: In order to carry out the research in an orderly and coherent way, a sequence of actions or steps is needed to be followed. The foremost work in this direction is selecting a topic for the research. While selecting the topic for research, the foremost task is to narrow down the puteriel mes among the available issues in that particular area of research.
While selecting research topic, the researcher should keep in mind that the research problem should be neither too broad nor too narrow. The research topic should be selected in a way that can be clearly defined and understood. Since, it is not a methodical step hence, selecting a research topic requires knowledge and significant time.
An efficient research study begins with a research topic. Research topic should be defined in such a way that the further stages can be carried-out effectively. As soon as the research topic and related questions are formulated, researchers proceed further to select research design and collect data. Hence, this step should be performed carefully, as it one of the most important foundations for making decisions.
2) Defining Research Problem: The next step of research process after selecting research topic is defining research problem. The research problem should be defined clearly and precisely. The research problem which is clearly defined solves half of the problem. Defining the research problem precisely for some researches is not possible. For example, defining research problem for poor sales is a difficult task, as it needs exploratory research to explore the area further.
A well-defined research problem is crucial for fulfilling the requirements of a research study. In this step, all the aspects of related to the research problem are identified after which a problem statement is formulated. Many crucial decisions are based on the problem statement. If the problem statement is defined precisely, then it helps the researchers to select the research design and data collection methods easily. Research problem should be defined in such a way so that all the time, money and effort put forward for the research does not go wasted. This is the most critical step in all the research process as improper definition of the research problem can cause the failure of entire research study.
3) Objectives of Research: After defining the research problem, the next stage is to set the research objectives. Research objectives defined in clear terms help the researchers to proceed in certain direction. It prevents the researchers from further distractions and enables them an issue to focus on. Research objectives construct the foundation for the research work. It is an essential ingredient of a research, as the entire effort and resources are applied to accomplish the research objectives. It helps the researchers to provide answers for the specific research questions. Thus, determining research objectives is the critical part of the research process as it supports the completion of the whole research. While defining research objectives the researchers should always remember that these should be comprehensive as well as attainable.
The objectives of the research are helpful in clarifying the type and level of information required for completing the research. This information requirement is further described by the nature of the research as well as by design used in the research. These objectives are the focal point of the any research as answering questions related to these objectives, would result in the completion of the procedure.
4) Literature Survey: The next step in the process of research is to analyse the available literature related to the research area. Available literatures allow the researcher to analyse the previously researches that have been published by different researchers in that field. The prime purpose of literature survey is to provide the researchers an idea about the area of knowledge and highlights the issues that needs be researched. Hence, surveying the literature is one of the most important steps in the research process.
Often literature survey provides data accumulated during a certain time-period. It generally has a specific organisational pattern, but it can also contain just the summaries of sources. While summary includes reviewing important information from different sources, the synthesis or combination of information is the reshuffling or rearranging of information. This helps the researchers in developing new interpretations from the old information. This literature review may also be useful in developing intellectual knowledge of the research area alongwith significant arguments or discussions. Literature survey guides the researchers to evaluate the sources, and recommends them to collect data from relevant literatures only.
5) Formulation of Hypothesis: When literature is thoroughly surveyed, the researchers move to the next step, i.e., formulation of hypothesis. To formulate research hypothesis, the prime task is to identify the potential variables of the study, after which relationship statement is formulated on the basis of an expected relation between the variables. This statement is more focused compared to the research objectives. For example, in case of research problem related to effect of violent content of TV on behaviour of children, the hypothesis may be formed as "Violent content of the TV is responsible for the aggressive behaviour of the children". Here violent content of the TV is independent variable and behaviour of children is dependent variable, and a positive relationship is predicted by the researcher.
The dependent and independent variables along with target population are also described with the help of hypothesis to make the research subject clearer. The collected data is analysed and tested to prove the hypothesis and establish a relation between variables.
6) Selecting Research Design: Next step in the research process is developing the research design. Research design allows the researchers to answer to the research questions in an accurate, economical, and objective manner. Any research design performs two major functions:
i) Preparing a structured plan outlining various methods and techniques required in conducting the research.
ii) Making sure that these methods and techniques are suitable for the research. It also ensures that these techniques will help in finding objective, precise, and suitable answers to the research questions. According to Kerlinger, this function is called "control of variance".
With the help of research design, a researcher is able to decide the necessary tasks to perform at each step of the research. This plan helps in effective utilisation of time and resources. Therefore, research design can also be referred as the blueprint of the research. Research design is prepared to regulate and control every step of the research, which is the most vital issue of any study. Hence, it is considered as one of the most crucial stages in the entire research process.
7) Sample Design: As soon as the design of research is selected, the next task is to select the sample design. Sample design sets a platform for effective data collection and analysis. A sample design is responsible for the effective selection of research samples. Selecting sample design affects many aspects related to the research work. Hence, selection of suitable sample design should be carefully performed.
Designing of sample includes many important decisions such as deciding the sample frames, selecting suitable sampling technique, determining sample size, etc. Sampling design should be performed in such a way that the quality of research is maintained in an economic way. Sample design permits the study of a representative part of the target population, which results in reduction of unnecessary utilisation of money, time, and effort. This representative part or sample provides useful information which represents the larger target population.
8) Collection of Data: After finalising the sample in the previous step, the required data is collected from the sample of population. Actually this step is an intermediary stage between theoretical and practical aspects of a research. In the beginning of the research process, a basic idea about a research problem is developed with the help of available knowledge. After the research problem is formulated, data collection is performed systematically. Without having accurate data about the research problem, it is not possible to complete a study as it works as a source of information helpful in getting the solution. The methods used for data collection depend on the type and nature of the research. The few common methods are surveys, interviews, observation, case studies, etc.
Before collecting the data it is necessary for the researcher to select the research area, define the research problem/question, and select samples. Data collection is done prior to the phase of data analysis and reporting. The data collected is analysed and used for either supporting or replacing the philosophies presented by earlier related researches. Data collection plays a crucial role in combining the theories with their practical applications.
9) Execution of Project: It is the next step in the research process after the collection of data. In this step, the real execution of the research takes place. It is also known as the implementation stage of the research process. This step is responsible for the systematic execution of the research in reasonable time. The correctness and reliability of the collected data depends upon the efficient and feasible execution of the research process. To ensure smooth execution of research project, structured questionnaire can be used, where the questions and answers should be machine-coded. Various types of interviews can also be selected for data collection, but the interviewers should be trained and skilled enough. In this step, the researcher ensures that the research is executed as per the pre-set standards. Research process should be executed in an ethical manner. There should be no restriction on publishing of collected data. Other important aspects of the execution step are interpreting data accurately, and designing suitable formats for presenting the findings to particular audiences.
10) Analysis of Data: After collecting data and successfully executing the fieldwork, the collected data are analysed. Data analysis is very essential to draw-out the required information from the raw data by making it organised and meaningful. Organising and analysing the data facilitates the researchers to understand the feature of sample. There are many techniques available to analyse the data. Sometimes during data analysis, researchers manipulate the data to get desired conclusions or outcomes. Therefore, it is very important for the researchers to pay attention to the data analysis process and the procedure through which outcomes are calculated.
Though data collection provides a lot of raw data, but these data are unorganised in nature. By analysing the data, data are organised in such a manner that it provides meaningful answers. For example, responses of a survey may be compared to know the number of individuals attending the survey as well as the approaches used by respondents to answer certain questions. Analysed data can be visualised with the help of graphs, charts, tables, etc. the graphical representation of data allows the researchers to rearrange and reorganise the data so as to minimise the effort put by the readers in searching the significant information. By showing the analysed data graphically, presentation becomes easy to understand.
11) Testing of Hypothesis: The next step after analysing the data is to test the previously formulated hypothesis. In this step, researchers perform certain statistical calculations to accept or reject the hypothesis. Based on the collected data, a suitable hypothesis about a probability distribution is chosen. This stage comes under the purview of statistics as the analysis is performed with the help of statistical techniques. The prime motive behind testing a hypothesis is to check its accuracy. By testing a hypothesis researchers can check whether it represents the population at large or not, as the hypotheses are formulated on the basis of sample. A hypothesis is said to be accurate if it shows the true differences and does not contain random sampling error. The true difference is measured by testing the hypothesis.
12) Generalisation and Interpretation of Data: As the collected data is analysed through different statistical techniques and methods, the final results should be given value and meaning. The meaning and valuation of the results depend upon the process of interpreting results. On the basis of interpretations, various conclusions and generalisations are made. Researchers can generalise the research results if they conduct the testing a number of times, and the outcomes are found similar every time. But, if there is no hypothesis, then the outcomes are explained on the basis of some theories or concepts: This explanation often triggers new issues for further researches.
Generalisation means applying the findings and conclusions of the research to the actual world. Outcomes from the research can be interpreted in two possible ways:
i) Drawing inference from the outcomes to develop theories or concepts. In this case, the results are concluded on the basis of a general statement.
ii) Examining the data empirically and applying it to the larger population. In this case, the general statement is applied to the bigger area.
The process for developing the general statement is same for both the cases, but the nature of statement differs according to the nature of research problem, i.e., theoretical or empirical. After analysing the data, researchers try to interpret the findings on the basis of theoretical and practical objectives of research.
Data interpretation is a step of research process where the measurements. and statistical observations of the study are scrutinised to develop evidences for responding to a research problem.
13) Preparation of Research Report: The final step of any research process is the preparation of research report. After collecting, analysing, and interpreting the data, the next task is to compile all the steps and present those phases in a written-form. It includes detailed description of research design, sample design, tools for data collection, and statistical techniques for the analysis of the collected data. Since, research report is very useful for current as well as further researchers, hence proper care must be taken while preparing the report.
Report writing needs skills and knowledge so that appropriate data can be appropriately represented. The report writing skills may be developed through practice, but a researcher should always follow the basic principles of report writing. Some of the important skills needed are clarity, coherence, objectivity, etc. a research report is efficient if it is able to communicate and present the research data. Usually, management as well as the audience is not interested in the details of statistical calculations and its procedures, hence, the researcher should try not to overload the report with such specifics. Therefore, much care is required for the effective preparation of research report to make it useful for the management and audience.
Significance of Research
Research plays a vital role for an organisation as it provides valuable information to the managers that help them in decision-making at various stages of operation. Research helps the management in following ways:
1) Recognises the Potential Opportunities and Threats: For any strategy to be successful, the organisation needs to have a very good understanding of the environment in which it operates. Research is a tool with which management is able to scan its environment and identify various opportunities and problems existing in the environment. By scanning and researching extensively, management can understand the environmental situations efficiently. This helps to formulate strategies in accordance with the situations to overcome the prevailing problems and exploit the opportunities to the fullest.
2) Assessment of Problems and Opportunities: Researching the problems and opportunities help the managers to estimate and analyse them. It allows the managers to identify the existing problems and the factors responsible for the problems. Research facilitates the managers in identifying, exploring, refining and quantifying the opportunities existing in the environment. Alongwith these, it helps in setting the priorities in case of multiple opportunities.
3) Selection of Best Alternative Action: Research assists the managers in selecting the best among the alternative courses of action. The various alternatives are evaluated using specific evaluation criteria set by the researcher. Researchers forecast the necessary future activities to be taken with properly analysing the scenario which in turn helps in planning. Research can also suggest the strategies that managers should use in planning properly and preventing it from failing. For example, a company can research the best possible strategy for positioning of a product.
4) Evaluating the Course of Action: Research can be used to see if the planned course of action has been implemented in way it was intended to. It allows the managers to estimate the extent to which a given activity or project is executed as per the direction. It helps to identify the potential factors that can affect the execution. Research is also carried-out to evaluate and control the strategies implemented for executing the project.
5) Analysing the Competition: The organisations need to study the market and the level of prevailing competition in it. To fulfil this objective, organisations conduct research to collect the information regarding the purchasing trends, competitor's strategy, market share of competitor firms, etc. This allows managers to formulate strategies that can help them in achieving their targets. For example, Pepsi Co. can conduct a research to know the strategies adopted by Coca Cola.
Limitations of Research
Unlike other nations, in India, the need and importance of research is not yet realised. Hence, it faces several barriers which are as follows:
1) Lack of Fund: Researchers need sufficient fund to conduct a research properly. But, companies do not sufficiently allocate funds for the research and development activities. Due to the lack of sufficient fund, several research projects either get delayed or do not proceed further.
2) No Centralised Database: There is no centralised database system available for research in India, due to which it is very difficult to find the information about already conducted related researches. The consequence of this barrier is the repetition in research works which is carried-out by different organisations.
3) No Coordination among Researchers: Research work requires a strong code of conduct to be followed. The researchers do not follow the norms due to which they have no coordination. This results in difference of opinion among them which in turn affects the quality of research work.
4) Lack of Library Management: The libraries in India are not managed properly. There is lack of books, journals, and reports in libraries, due to which the crucial time of researchers are wasted in finding the useful information from available material.
5) Absence of Ethics in Research: Researchers in India have no proper knowledge about the domain due to which they copy the material from other research works instead of conducting the research on their own. As a result, the accuracy and validity of the research outcomes are highly unreliable. The absence of ethics in research is one of biggest problem that can be solved by following the ethical norms while researching.
6) Lack of Proper Contacts between Research Departments: Research is a well co-ordinated activity of the concerned departments conducting it. The lack of coordination among the researchers of the related departments leads to biasness in the research. Due to this barrier research works lack. the huge amount of primary data may remain unavailable to the researchers which may hamper the quality of research.
7) No Trust on Researchers: Many of the organisations do not cooperate with the researchers due to lack of trust. Companies show unwillingness to share information, because of the risk of misuse of data.
8) Lack of Skilled Researchers: Research is a systematic procedure and requires the researcher to be well- trained in collecting data, sampling and analysis. But, the researchers in India have no expertise in research methodology. Most of the research guides have no knowledge regarding the tools and techniques used in research. This lack of skilled manpower is a big limiting factor in the research environment in India, as it directly affects the reliability of research work being done. Hence, the organisations should train their researchers in specified area of knowledge.
9) Data Manipulation: Researchers often manipulate the data to present it the way they want. The reason behind this manipulation is the lack of confidence on the outcome of the research activity. This results in a false picture of a research work and leads to severe impact on both the accuracy and validity of research. The researchers conduct their activities on the basis of mere theoretical knowledge which is not sufficient, since the knowledge of theory and its application are two different aspects. Hence, a proper knowledge of theory as well as correct practical implementation is necessary for a good research work.
10) Costly Affair: Printing and publishing the research work proves to be costly for the research associates. If the research paper is to be published internationally then it requires more fund, which is not affordable for many researchers.
Research in an Evolutionary Perspective
The criterion or basis for investigating the world was developed very late. Initial methods of investigation emphasised by the Greek philosophers, like Aristotle who claimed that the teeth in both men and women differ in numbers. He gave detailed and comprehensive reasons to support this claim but never examined it. In fact, evidence and not arguments is needed to determine the accuracy of any statement. Therefore, since that time onwards, observations and experiments have started to be undertaken. This meant that the conclusions of the experiments were universal and could be replicated. In this way, evolution of scientific method took place. It was later followed by experiments in the field of behavioural sciences. Similarly, statistics, decision theory, game theory and theories of probability, utility, operations became the basis for social and empirical sciences. Solutions to the common problems of methodology were sought by several scientific philosophers. These problems included validation of induction and nature of scientific explanation.
Before the evolution of research could flourish, a two hundred years long battle took place between emerging empiricism and the established church. Slowly, with the growth of science, the attitude of the Western people began to shift from medieval end towards modernity. This growth became possible due to the efforts of early scientists like Copernicus who supported the view that the Earth revolved around the sun based on empirical evidence and challenged the view that Earth was at the centre of the universe. Another scientist Francis Bacon believed that experiments and not mere assumptions should be considered as the medium of increasing the level of knowledge. Techniques of mathematics and observation were used by Kepler that replaced the Pythagoras theorem and proved that the planets revolve in elliptical orbits. Galilei supported the view of Copernicus and hence, was put under house arrest. Another scientist Descartes argued that there was a scientific explanation behind the existence of God and human beings. He believed in the Cartesian rationalism that put faith in the existence of God as well as supported experiments and observations. Our understanding about nature and its various patterns was further enhanced by the experiments of Newton.
There are several claims which state that the scientific methods are the most convincing form of research. They are unbiased and allow the researcher to not follow the preconceived theories and notions rather one can possibly conduct new experiments in order to examine the accuracy of the conclusions. Hawking proposed that the following two requirements should be satisfied by any theory in order to be considered as good one:
1) Certain forecasts must be made by the theory about the conclusions of future experiments.
2) The theory must accurately take into account a large class of observations which should be based on a model comprising less number of random elements.
Hawking believed that a physical theory is a mere hypothesis which is always temporary and cannot be proved. Therefore, there is always a chance that a conclusion will contradict with the theory, no matter the number of times it has agreed with it in succeeding experiments. But, only a single contradictory observation is required to prove a theory wrong. Therefore, it can be said that a new theory is an extrapolation of the former one. Practically, add-ons in the form of modifications and rejections are done in the former theory in order to develop a new one.
To prove the above point, an example can be taken where the gravitational laws of Newton were challenged by the predictions of Einstein. The theory of gravitation given by Newton in 1666 is among the greatest rational discoveries of all time. Each and every observed fact was explained in this theory. It also made forecasts which were tested and found accurate later on, under the assumption that the instruments used to test were accurate. But, certain discrepancies were found in this theory of Newton in the 19th century when more accurate testing. instruments were used. After this, Einstein opposed the theory of Newton and gave his own theory of relativity. However, this does not mean that there is a difference in the truth discovered by both Newton and Einstein for the same universe. It simply means that all the experimental evidences at that time agreed with the theory, thereby proving it to be true.
A new theory is developed by the researchers every time an old theory is unable to prove new data. This is not an easy task in the time where knowledge is increasing and the new theory proposed has to include the results of past researches as well as prove the new data. In fact, researchers have to study and reject a lot of assumptions and hypothesis before formulating a new theory. Discussions are conducted regarding the validity, various hypothesis (formed on the basis of distinct assumptions) are approved and later on rejected. For example, Copernicus proposed that the planets of our solar system revolve around the sun in a circular motion, but according to Kepler, they revolve in an elliptical form. After carefully examining the revolution pattern of the planets, it was found that Kepler's theory was more accurate and the planets actually revolve in ellipses. Hence, the theory given by Copernicus was replaced by the one given by Kepler. However, it is possible for different theories to have similar forecasts. If the new experimental evidence contradict with the forecasts of a long accepted theory, then it might be rejected based on the explanation of reality. However, such theory might still be applicable under certain limitations. For example, the theory of relativity given by Einstein replaced the laws of motion given by Newton. This was because Einstein's theory gave a more accurate and general understanding of the universe.
Creation of knowledge is an age old concept and it forms the basis for the development of society. The researches that are conducted leads to new inventions and discoveries. It also assists in technology development and provides fresh knowledge and guidelines.
Final Notes
As we conclude this insightful exploration on the significance of research from an evolutionary perspective, GuideFlare.com remains committed to fostering a culture of curiosity and evidence-based exploration. Research is a testament to the indomitable human spirit, constantly evolving to seek solutions to complex challenges and unearth the wonders of our universe. Let GuideFlare.com be your guiding light, igniting the flame of knowledge and inspiring you to contribute to the ever-expanding tapestry of human understanding. Together, let us forge ahead, fueled by the power of research, towards a future enriched by wisdom and discovery.
